You might not know it, but die casting1 is a process that is all around you every day. Not understanding this key manufacturing method means missing out on a powerful tool for your products.
Die casting is a manufacturing process that makes strong, precise metal parts by injecting molten metal into a mold. A common example is a car’s transmission housing or an electric vehicle’s motor casing. The process creates complex shapes with smooth surfaces, making it ideal for durable, mass-produced components.
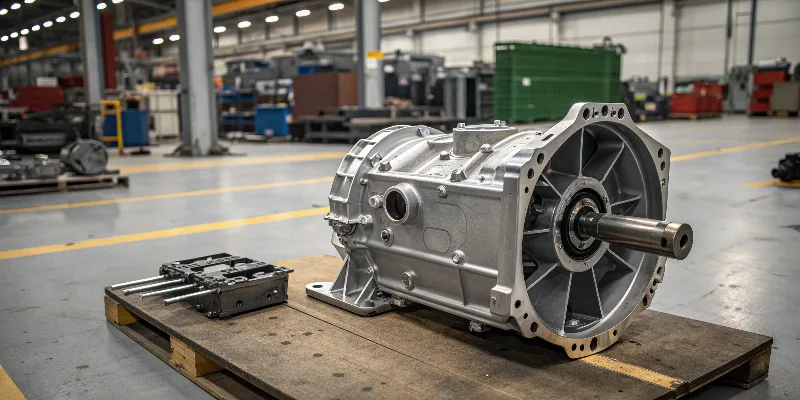
Die casting is a process that has been used for more than a century, but it has never been more relevant than it is today. As an engineer who has worked in this field for over 20 years, I see its applications in almost every industry. Let’s look at some examples you probably interact with every day and then dive into the reasons why this process is so valuable for modern manufacturing.
What Are the Most Common Products Made by Die Casting?
Die casting is not just for huge industrial parts. It is used all around you, from your car to your kitchen. Ignoring these simple examples means you’re missing the true scope of the technology’s application.
Common products made by die casting include parts for automotive engines and electronics. You will also find them in power tool housings, LED lighting fixtures, and components for home appliances. The process is used for any product that needs strong, precise, and complex metal parts in high volume.
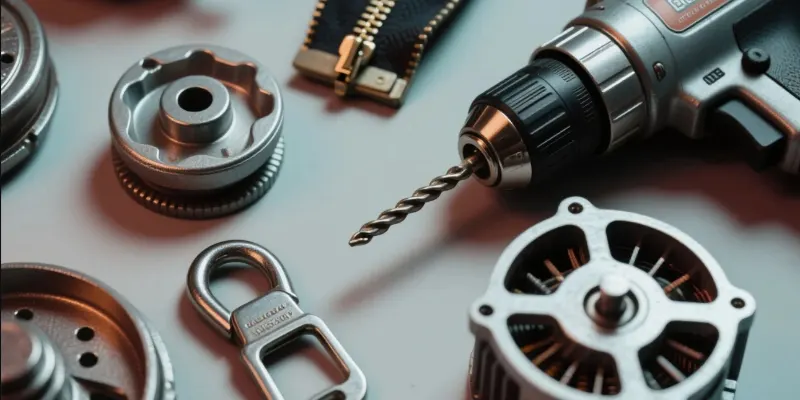

In my early career, I worked in the workshop, repairing mold2s and adjusting machines. We produced parts for everything from lawnmower engines to washing machine components. The sheer variety of products that rely on this process is remarkable.
The "Invisible" Parts
Many die-cast parts are hidden from view. They are the internal components3 that make a product work. For example, the solid metal frame of a power tool, the heat sink in a computer server, or the pump housing in an industrial machine are all likely die-cast. The process is essential for creating high-performance products at a large scale.
High Volume and Consistency
The reason die casting is so common is its efficiency. Once a mold is made, the process can produce thousands or even millions of identical parts very quickly. This consistency and speed make it the perfect solution for consumer goods4 and industrial equipment that must be produced in massive quantities.
How Is Die Casting Applied in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry5 is always pushing for lighter, stronger, and more efficient parts. How has die casting become a foundational technology in this fast-moving field?
Die casting is used in the automotive industry for critical components like engine blocks, transmission cases, and wheels. For electric vehicles, it is essential for producing lightweight battery housings and complex motor casings that help reduce vehicle weight and improve driving range.
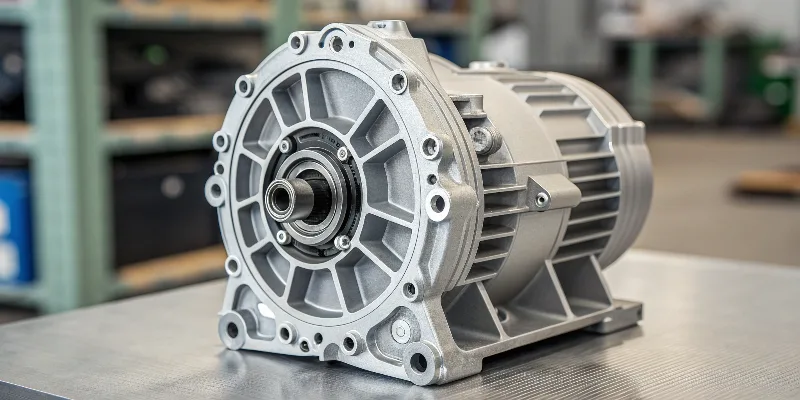
I have spent the last half of my career working on projects for the automotive industry. The shift from traditional engine blocks to lightweight EV parts has been a major change. My team and I have led the development and production of multiple new energy vehicle projects, and we rely on die casting every day.
From Traditional to Next-Gen
While internal combustion engine components like engine blocks and oil pans have been die-cast for a long time, the move to electric vehicles has created new opportunities. The EV battery pack needs a strong, lightweight housing. The motor and its electronics need a casing that can dissipate heat efficiently. Die-cast aluminum6 is the ideal material for these new demands.
The Rise of Giga Casting
For some parts, the process is even bigger now. Automakers are using "Giga Presses7," which are huge die casting machines. These machines can make massive, single-piece castings, like a car’s entire rear underbody. My team and I work with clients who are using these parts to simplify their vehicle assembly process, which saves time and money.
| Automotive Part | Die Casting Benefit |
|---|---|
| Engine Blocks | Provides strength, lightweighting, and integrated passages. |
| EV Battery Housing | Offers thermal management, structural integrity, and low weight. |
| Structural Shock Tower | Replaces multiple parts with one large, strong casting. |
What Everyday Consumer Goods Use Die Cast Parts?
You likely hold a die-cast part in your hand almost every day. It’s in your office, your home, and your garage. Have you ever noticed them, or considered how they were made?
Die-cast parts are found in many everyday consumer goods. Examples include the strong metal bodies of power drills, complex parts inside blenders, the handles of kitchen appliances, and even zippers and fishing reels. They provide strength and a high-quality feel.
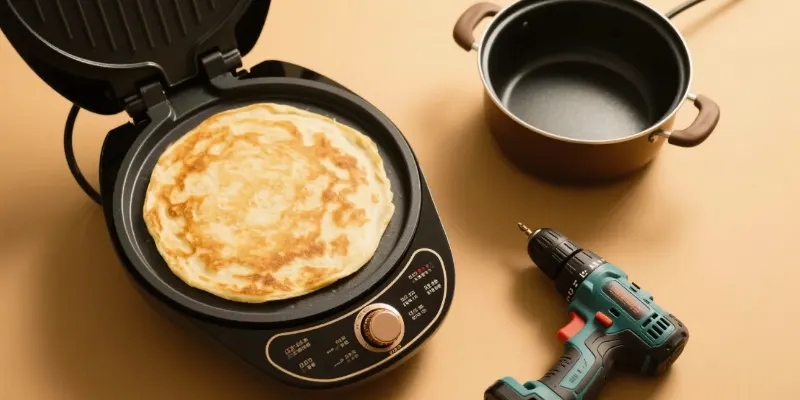

The versatility of die casting is what makes it so useful. It is not just for huge industrial applications. It is for any product that needs to be durable, look good, and be produced in high volume.
Durability and Aesthetics
Die casting is not just about making a functional part; it is also about making a part that looks and feels good. The process can create a smooth surface finish8 that is ready for plating, painting, or powder coating. This is why die-cast parts are used for high-end handles, faucets, and decorative items.
Mass Production and Cost
For a product that needs to be produced in millions of units, the cost of each part is a major concern. Die casting has a very fast cycle time, and the molten metal can be almost entirely recycled. This makes it a very cost-effective9 choice. I have worked on molds for small components like zipper pulls that had to run all day, every day, to meet the customer’s high volume needs.
Why Is Aluminum the Most Popular Material for Die Casting?
Die casting can use many different metals. But one material is a clear leader. Understanding why aluminum is so popular is key to understanding modern manufacturing.
Aluminum is the most popular material for die casting due to its excellent combination of properties. It is extremely lightweight, has a very high strength-to-weight ratio, and offers superior thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. These factors make it ideal for modern components.
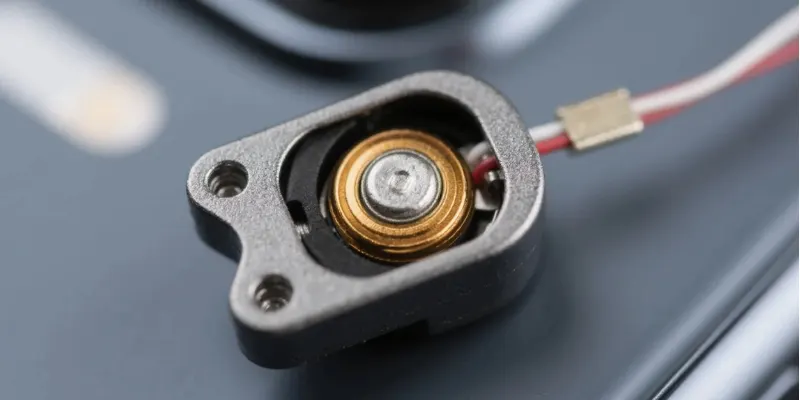

In my work on EV components, I see how important aluminum’s properties are every day. Its ability to dissipate heat is as important as its low weight. A motor controller housing needs to keep the electronics cool, and die-cast aluminum is the perfect solution.
The Right Balance of Properties
No single material is perfect for every application. But aluminum offers a balance that is hard to beat.
| Aluminum Property | Benefit in Die Casting |
|---|---|
| Low Density | Makes parts lightweight, which is crucial for efficiency. |
| High Strength | Provides durability and structural integrity for critical parts. |
| Thermal Conductivity | Dissipates heat from motors and electronics effectively. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Ensures long-term reliability without extra surface treatment. |
What Are Examples of Complex Shapes Achieved with Die Casting?
Die casting can create shapes that are impossible to make with other methods. From intricate details to internal channels, it allows for incredible design freedom for engineers.
Die casting can create complex shapes with thin walls, internal passages, and integrated features like mounting bosses. Examples include engine blocks with internal cooling channels and complex aluminum housings for electronics that combine multiple functions into a single, cohesive part.
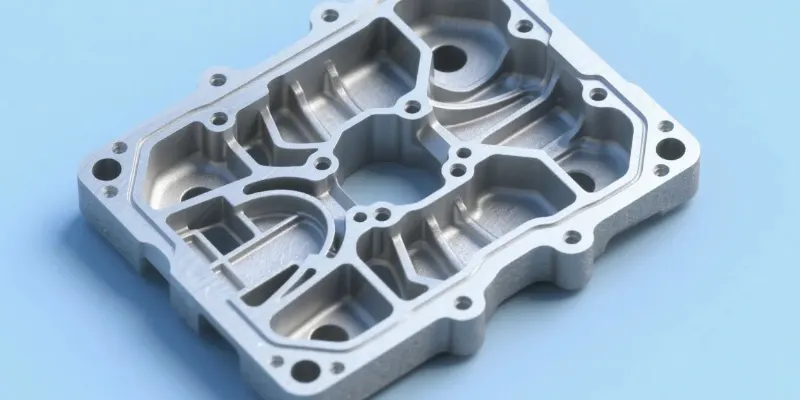

One of the biggest advantages of die casting is its ability to produce what we call "net-shape" parts. This means the part comes out of the mold almost exactly as you need it to be, with minimal or no need for extra machining. This saves a lot of time and money in the production process.
Combining Functions
Engineers can design a single die-cast part that combines features that would normally require a multi-part assembly. This can mean a part with integrated ribs for strength, cooling fins for heat dissipation, and mounting points for other components, all in one piece. This reduces weight and labor costs.
Precision and Tolerances
For my clients who are Supplier Quality Engineers, like Jure, this is a huge benefit. Die casting can achieve very tight dimensional tolerances and a smooth surface finish directly from the mold. We work to very strict PPAP standards. The precision we can achieve directly from the die is a critical factor in meeting those requirements.
How Does Die Casting Compare with Other Manufacturing Methods?
There are many ways to make a metal part. How do you know when to choose die casting over forging, machining, or sand casting? Making the wrong choice is a costly mistake.
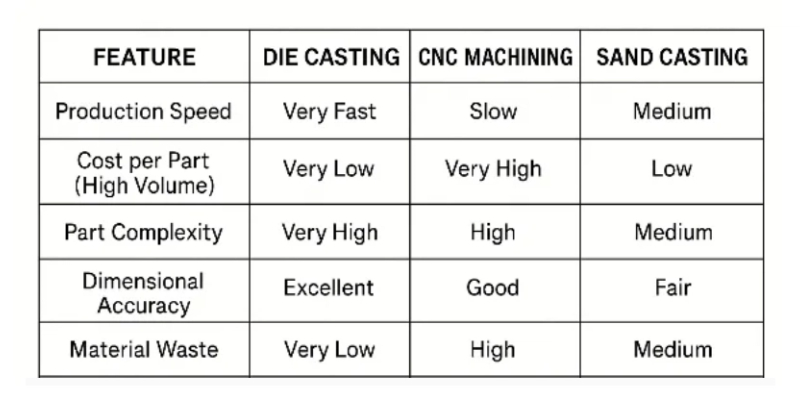
Compared to other methods, die casting is faster and more precise for high-volume production. It is more cost-effective than CNC machining and produces parts with finer detail and a better surface finish than sand casting or forging. This makes it ideal for large-scale, intricate parts.
As an engineering10 consultant, a big part of my job is helping clients choose the right process. The decision often comes down to a few key factors: production volume, part complexity, and required tolerances.
When to Choose Die Casting
You should choose die casting when your project has a high production volume and requires parts with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and a good surface finish. The initial cost for the mold is high, but the cost per part drops dramatically in high volume.
| Feature | Die Casting | Sand Casting | CNC Machining | Forging |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Per Part (Volume) | Very Low (High Volume) | Very Low (Low Volume) | High | Medium |
| Tooling Cost | High | Low | None (Digital File) | High |
| Detail & Tolerance | Excellent | Fair | Excellent | Good |
| Cycle Time | Very Fast (Seconds) | Slow (Minutes) | Slow (Hours) | Fast (Seconds) |
Conclusion
Die casting is a foundational manufacturing process. Its ability to create precise, complex, and durable parts in high volume makes it an essential tool for engineers and buyers in countless industries.
-
Explore the fundamentals of die casting to understand its significance in manufacturing. ↩
-
Learn about the mold-making process and its importance in die casting. ↩
-
Learn about the hidden yet crucial parts produced through die casting. ↩
-
See how die casting is present in everyday items, enhancing their durability and quality. ↩
-
Learn how die casting revolutionizes automotive manufacturing with lightweight and efficient components. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of aluminum in die casting and its impact on modern manufacturing. ↩
-
Learn about the innovative Giga Presses and their impact on automotive manufacturing. ↩
-
Understand how surface finish affects the aesthetics and functionality of die-cast parts. ↩
-
Explore the cost benefits of die casting, especially in high-volume production scenarios. ↩
-
Explore the engineering principles that make die casting a preferred manufacturing method. ↩




